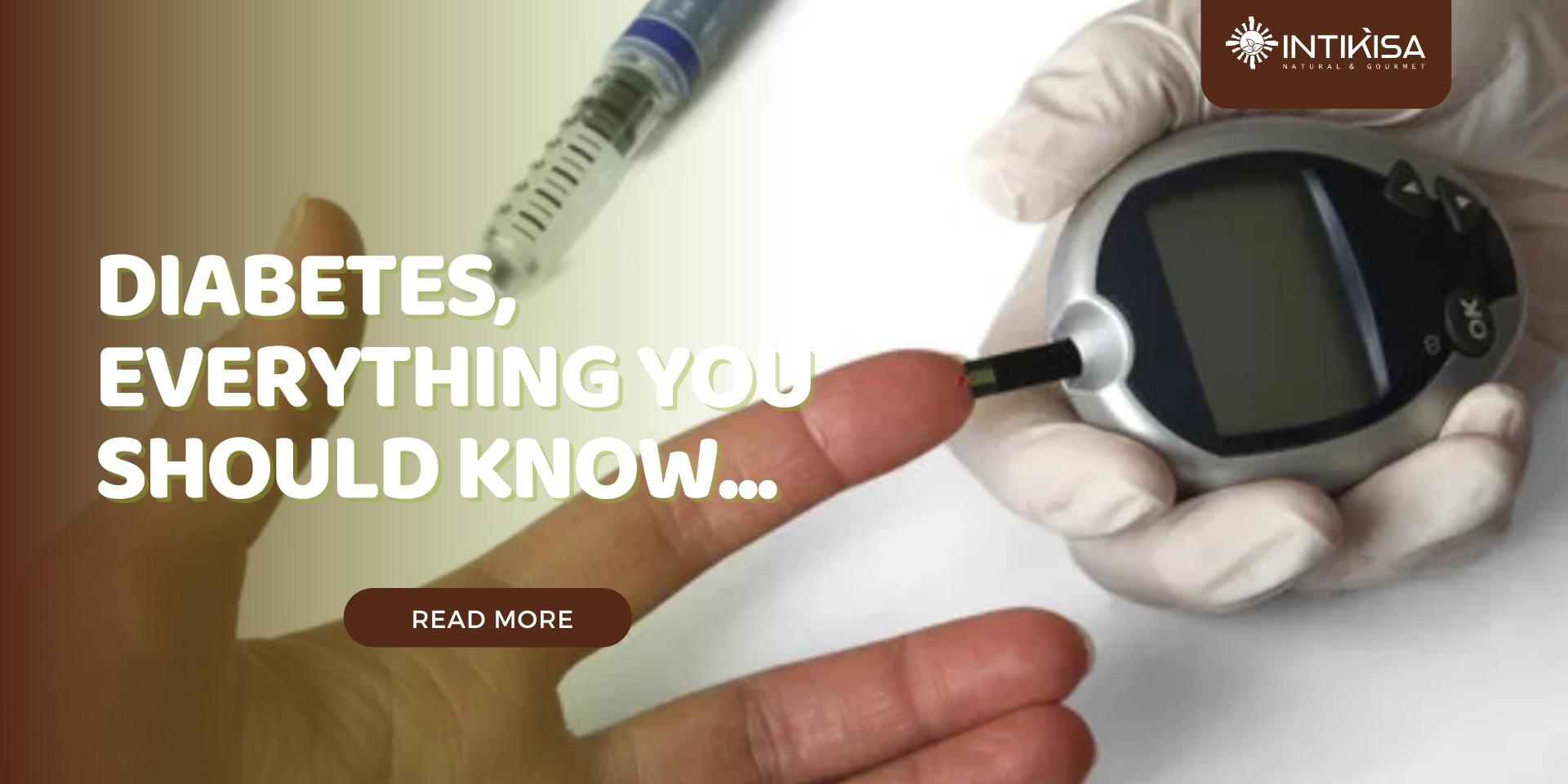
Diabetes is a disease that occurs when the level of glucose (also called blood sugar) in the blood becomes too high. Blood glucose is the main source of energy obtained from food. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps glucose from food to enter cells for energy. Sometimes the body doesn’t make enough insulin, or doesn’t make or use it properly, and glucose stays in the blood and doesn’t get to the cells.
What types of diabetes are there?
Type 1 diabetes . Its origin is still not very clear, it is suspected that there is an autoimmune reaction that causes the body’s own defenses to attack the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas, which gives rise to a deficiency of this substance. People with it need daily injections of insulin to control their blood glucose levels, without which they could not survive.
Type 2 diabetes . It is the most common type of diabetes, since it covers, according to data from the Diabetes Foundation, between 85% and 90% of all cases. When you have type 2 diabetes, your body can make insulin, but it doesn’t make the right amount or isn’t able to respond to its effects, causing glucose to build up in your blood.
Gestational diabetes . During pregnancy it can happen that the hormonal changes typical of this state cause a blockage of insulin function. When this happens, glucose levels can rise in a pregnant woman’s blood. It usually presents late in pregnancy and affects about 5% of pregnant women.

What complications does diabetes cause?
Diabetes increases the risk of the following serious health problems, although with proper treatment and recommended lifestyle changes, their onset can be prevented or delayed.
Cardiovascular diseases . High blood pressure, high cholesterol, and high blood sugar can increase the risk of complications such as angina, heart attack, stroke, peripheral arterial disease, and heart failure. In fact, two thirds of people with diabetes die from a heart attack or stroke.
Kidney disease . The kidneys are another organ affected by diabetes, since the gradual deterioration of the small blood vessels can make them less efficient or completely damaged.
Eye diseases . People with diabetes have a higher risk of blindness than healthy people. This problem can cause a sudden or progressive loss of vision and can also lead to a retinal detachment.
Nerve injuries . This can generate pain, tingling and loss of sensation, which makes the lesions go unnoticed and causes serious infections and ulcers, diabetic foot and amputations. Approximately half of people with diabetes have some form of neurological damage, although it is more common in those who have had the disease for several years.
Skin problems . Up to 33 percent of people with diabetes experience common skin conditions, such as bacterial or fungal infections and itching, that are caused or affected by diabetes at some point in their lives.
How can I prevent or delay the onset of diabetes?
If you are at risk of diabetes, you can prevent or delay it. Most of the things you should do are related to a healthier lifestyle. Making these changes will also have other health benefits. You can lower your risk of other diseases and feel better and have more energy. The changes are:
Lose weight and keep it off . Weight control is an important part of diabetes prevention. You can prevent or delay diabetes by losing 5-10% of your current body weight. For example, if you weigh 200 pounds (90.7 kg), your goal is to lose 10 to 20 pounds (4.5 to 9 kg). Once you’ve lost weight, it’s important to keep it off.
Follow a healthy eating plan . It’s important to reduce the number of calories you eat and drink each day, so you can lose weight and keep it off. To achieve this, your diet must include smaller portions and less fat and sugar. You should also eat foods from each food group, including lots of whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
Exercise regularly . Exercise has many health benefits, including helping you lose weight and lowering your blood sugar levels. Try to get at least 30 minutes of physical activity five days a week. You can start slowly until you reach your goal.
Don’t smoke . Smoking can contribute to insulin resistance, which can lead to diabetes.